The unit of measure for the amount of heat is the formula. Quantity of heat. Heat units. Specific heat

What process is called heat conduction? In what environments is it possible? Is it the same for various substances? What process is called convection? In what environments is it possible? What determines the rate of convection? What process is called radiation. What features of this type of heat transfer do you know?

The energy that heat receives or loses during heat transfer is called the amount of heat. Symbol: Q Units: joule (J) (kJ) calorie (cal) 1 cal=4.19 J 1 kcal= 4190 J 4.2 kJ Calorie is the amount of heat required to heat 1 g of water by 1°C .

Stage 1 of the experiment 1. Pour water into the flasks: the second one is 2 times more than the first one. 2. Fix the flasks in the legs of the tripods 3. Measure the initial temperature of the liquid in each flask. 4. Light spirit lamps. 5. Simultaneously start heating the flasks. 6. Measure the temperature in each flask after 2 minutes. 7. Make a conclusion.
![]()
An experiment to determine the dependence of the amount of heat transferred to a substance on the mass of this substance. m 1 
Stage 2 of the experiment 1. Pour an equal amount of water into 2 flasks. 2. Fix the flasks in the legs of the tripods 3. Measure the initial temperature of the liquid in each flask. 4. Light spirit lamps. 5. Simultaneously start heating the flasks. 6. Without removing the thermometer from the liquid, stop heating when the temperature in the first flask rises by 20°C, and in the second by 25°C. 7. Measure the time it took for each process. 8. Draw conclusions.

An experiment to determine the dependence of the amount of heat transferred to a substance on a change in its temperature. m 1 = m t 1 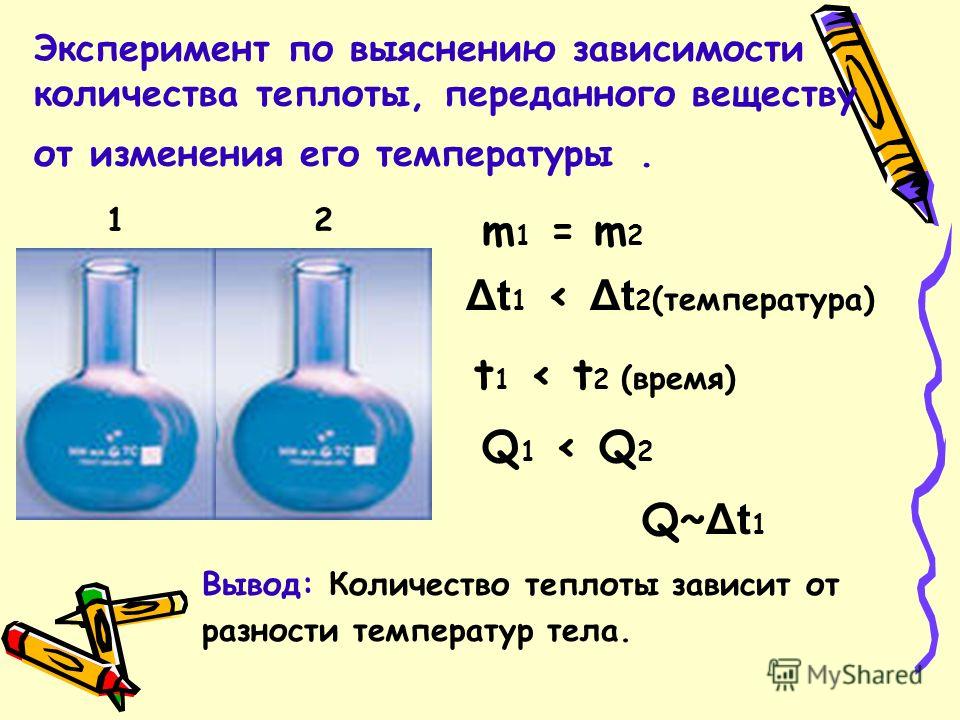
Stage 3 of the experiment 1. Pour an equal amount of water and oil into 2 flasks. 2. Fix the flasks in the legs of the tripods 3. Measure the initial temperature of the liquid in each flask. 4. Light spirit lamps. 5. Simultaneously start heating the flasks. 6. Measure the temperature in each flask after 2 minutes. 7. Make a conclusion.

T 2 (time) Δt 1 = Δt 2 (temperature) Q 1 > Q 2 transferred from its kind m 1 = m 2 1 2 t 1 > t 2 (time) Δt 1 = Δt 2 (temperature) Q 1 > Q 2 Conclusion: the amount of heat that is necessary to heat (cool) the body depends on the type of substance" class="link_thumb"> 11 !} An experiment to determine the dependence of the amount of heat transferred on its kind. m 1 = m t 1 > t 2 (time) Δt 1 = Δt 2 (temperature) Q 1 > Q 2 Conclusion: the amount of heat that is necessary to heat (cool) the body depends on the type of substance. 1 2 Q ~ on the type of substance t 2 (time) Δt 1 = Δt 2 (temperature) Q 1 > Q 2 Conclusion: the amount of heat that is necessary to heat (cool) the body depends on the type of substance "> t 2 (time) Δt 1 = Δt 2 (temperature) Q 1 > Q 2 Conclusion: the amount of heat that is necessary to heat (cool) the body depends on the type of substance. 1 2 Q ~ on the type of substance "> t 2 (time) Δt 1 = Δt 2 (temperature) Q 1 > Q 2 Conclusion: the amount of heat that is necessary to heat (cool) the body depends on the kind of substance" title="(!LANG: An experiment to determine the dependence of the amount of heat transferred on its kind. m 1 = m 2 1 2 t 1 > t 2 ( time) Δt 1 = Δt 2 (temperature) Q 1 > Q 2 Conclusion: the amount of heat that is necessary to heat (cool) the body depends on the type of substance"> title="An experiment to determine the dependence of the amount of heat transferred on its kind. m 1 \u003d m 2 1 2 t 1\u003e t 2 (time) Δt 1 \u003d Δt 2 (temperature) Q 1 > Q 2 Conclusion: the amount of heat that is necessary to heat (cool) the body depends on the type of substance"> !}
Designated: s unit of measure: J/kg °C Physical quantity, numerically equal to the amount of heat that must be transferred to a body of mass 1 kg in order for its temperature to change by 1 ° C, is called specific heat substances. Specific heat substances.

The specific heat capacity of steel is equal to 500 J/kg °C. This means that for heating (cooling) steel m = 1 kg per 1ºС, an amount of heat equal to 500 J is required. The specific heat capacity of a substance in different states of aggregation is different. for example, for water c = 4200 J/kg °C; for ice c = 2100 J/kg °C


Fixation What is the amount of heat? What is measured? What determines the amount of heat? What is the specific heat capacity of a substance? What is the unit of specific heat capacity. The specific heat capacity of lead is 140 J/kg °C. What does this mean?

What is the specific heat capacity of zinc, brick, water? How much heat must be imparted to these substances with a mass of 1 kg in order to heat up by 1 ºС. Calculate the amount of heat (in calories and kilocalories). Required to heat water by 1°C, the mass of which is 3; 4 kg.


