Accounting info. Accounting info Reflection in USN 1s 8.3
For organizations that use the simplified taxation system (hereinafter referred to as the simplified taxation system), it is necessary to create a book of income and expenses (hereinafter referred to as KUDiR). To automatically generate KUDiR records in the 1C:Manufacturing Enterprise Management (1C:UPP) program, you first need to set up an accounting policy for accounting and tax accounting.

On the “General” tab, you must select the taxation system - Simplified. Next, go to the “STS” tab. Here you need to select the object of taxation: Income or Income minus expenses, indicate the date of transition to the simplified tax system, the number and date of the notification of the transition to the simplified tax system.

When you select the tax object “Income minus expenses”, the “STS Expenses” tab becomes available.

On this tab, the conditions for recognizing expenses are established, i.e. it is determined which events must occur for expenses to be recognized in order to be accepted for tax accounting.
To generate entries in the Income and Expense Book in 1C:UPP, the following registers are used:
The accumulation register “Mutual settlements of the simplified tax system” for monitoring mutual settlements with counterparties, accountable persons, and employees. Accounting is carried out with detail up to the settlement document.
Accumulation register “Expenses under the simplified tax system” for accounting expenses. Expenses are taken into account by type of expense (items, services, additional expenses, wages, taxes, etc.), expense elements (elements of the directory Nomenclature, Individuals, etc.), settlement documents, batches, payment statuses, reflection order in NU (Accepted, Not Accepted, Distributed), etc. Expenses are written off using the FIFO method.
Accumulation register "Book of income and expenses." This register stores KUDiR records, from which the Income and Expense Accounting Book is subsequently formed.
Create a Book of Income and Expenses you can generate the report “Income and Expense Accounting Book” (menu Reports-Accounting and Tax Accounting) (the report is generated according to the accumulation register data “Income and Expense Accounting Book”).

Also, to check the correctness of the formation of KUDiR, you can generate a report “Analysis of the state of tax accounting according to the simplified tax system” (the report is generated according to the data of the accumulation register “Book of records of income and expenses”).

In this report, all income and expenses are divided into sections. A transcript is available for each section. (the transcript is generated according to the accumulation register “Expenses under the simplified tax system.”)
Let's take a closer look at some of the sections.
Receipts from buyers.
This section contains data on receipts of funds from customers, for example, documents “Incoming payment order” with the transaction type “Payment from buyer” or “Cash outflow order”. A transcript of this section is presented below:

Products and materials.
This section includes data on expenses by type of accounting “Nomenclature”, for which the reflection in the NU upon receipt is set to “Accepted”.


For each item, you can also display a transcript in which receipts, payments, write-offs and recognition of expenses are reflected graphically and according to documents.


Let's look at how entries get into the Book of Income and Expenses by item. To do this, let’s take a closer look at the accounting policy settings:

By default, in order to be included in expenses for the purchase of goods and materials, there are 2 prerequisites:
1) Receipt of goods (materials) - documents “Receipt of goods and services”, “Advance report”.
2) Payment for goods (materials) to the supplier – “Outgoing payment order”, “Cash outgoing order”.
After these 2 conditions are met (the presence of both documents), expenses for the purchase of goods fall into the Income and Expense Accounting Book.

You can also select 2 additional conditions in your accounting policy:
For materials:
3) Transfer of materials to production - “Demand-invoice”. When this flag is set, expenses for the purchase of materials are considered recognized only after the “Requirement-invoice” document has been posted.

4) Product output – document “Production Report for a Shift”.
For goods:
3) Sales of goods – document “Sales of goods and services”.
4) Receiving income (payment from the buyer).

Third-party company services
This section contains information about services. To be accepted as an expense, 2 conditions must be met: reflection of the provision of the service (“Receipt of goods and services”) and payment to the supplier.

In this example, services were received in the amount of 200,000 rubles, but 150,000 rubles were paid to the supplier, therefore, expenses were recognized only in the amount of 150,000 rubles, and 50,000 rubles. remained unrecognized, therefore they will be included in expenses only after the next payment.
Additional costs for the acquisition of inventory items.
To reflect additional expenses in the Income and Expense Book, you must also consider the accounting policy settings:

Mandatory conditions for recognizing expenses are the receipt of additional expenses (the document “Receipt of additional expenses”) and payment to the supplier.
An additional condition is the write-off of inventories; in this case, additional expenses will appear in the Income and Expenses Accounting Book only after the write-off of inventories (goods or materials) to the cost of which the additional expenses were attributed.
Salary.
This section reflects labor costs. Explanation of this section allows you to see information by employee.

The report shows the initial balance, accruals (amount of accruals - personal income tax), payments, final balance, as well as the amount accepted for expenses.
To accept payroll costs as expenses, it is necessary to reflect the payroll (“Reflection of wages in registration accounting”), where in the Reflection in NU column “Accepted” will be selected, and the payment of wages must also be reflected (“Outgoing payment order” with the type of operation “Transfer of wages”, “Expense cash order” with the type of operation for payment of wages).

Taxes, contributions and personal income tax
This section reflects the costs of paying taxes and contributions.

To be accepted as an expense, it is also necessary to reflect the fact of tax accrual (“Reflection of wages in registered accounting” with the Reflection type in NU “Accepted”) and the payment of taxes (“Outgoing payment order” with the transaction type “Transfer of taxes”).
other expenses
This section includes all other types of expenses, for example, transactions entered in documents “Cash expenditure order” with the transaction type “Other cash expenditure”, “Payment order for debiting funds” to reflect bank service transactions and others.
It is worth noting that in cash flow documents (payment orders, cash orders), the KUDiR button is available for some types of transactions, which allows the user to manually determine the content of the transaction and the amount of income or expenses, incl. accepted.


Also, an entry in the Income and Expense Book can be entered manually using the document “Entry in the Income and Expense Book (Manual Account)”

When using the Advanced Cost Accounting Analytics mode to generate income and expense ledger entries, you must run the “Restore the sequence of the simplified taxation system” process. You must select an organization and set the update date, then click the “Run” button.

In conclusion, it is worth noting that for the correct formation of entries in the book of income and expenses, a necessary condition is the restored sequence of document processing, because Often documents are entered retroactively, so at the end of the period it is necessary to sequentially re-enter all documents.
Thank you!
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides certain conditions for the recognition of expenses for taxpayers who apply the simplified tax system and who have chosen income minus expenses as the object of taxation. "1C: Accounting 8" monitors the fulfillment of these conditions, how - read in the proposed article prepared by specialists of the Alliance Soft company.
To automate accounting under the simplified taxation system, the management of the Absolut-XXI LLC Company chose the software product "1C: Accounting 8", which allowed us to solve the main problems:
- the ability to maintain a general and simplified taxation system in one program, in case of a change in the taxation system in the future;
- speeding up the process of data entry and processing;
- automatic generation of a book of income and expenses based on entered documents and manual entries.
In application solutions (standard configurations) from 1C, intended for organizations using a simplified taxation system, accounting is fully supported. This is necessary, first of all, for the organization itself to make a decision by the owners on the distribution of net profit and the accrual of dividends and income from participation.
The company "Absolut-XXI" LLC chose "Income reduced by the amount of expenses" as the object of taxation. In this case, in order to recognize expenses in order to reduce the tax base, it is necessary:
- monitor the fulfillment of all conditions for their recognition;
- correctly determine the moment of recognition of expenses;
- create an entry in the books of income and expenses when recognizing these expenses.
To solve these problems, “1C: Accounting 8” maintains tax accounting of expenses (according to the simplified tax system). Consistent completion of the relevant documents will allow the automatic generation of a book of income and expenses at the end of the reporting (tax) period.
Setting up accounting according to the simplified tax system will be carried out in the form "Accounting policy (tax accounting)" (menu "Enterprise" -> "Accounting policy" -> "Accounting policy (tax accounting)"), where on the "Basic" tab the flag "Use of a simplified system" is set taxation", which makes the "STS" tab available for filling out. On this tab, the object of taxation is determined: “Income” or “Income reduced by the amount of expenses” and the procedure for recognizing expenses (the composition of events, the occurrence of which is a prerequisite for recognizing an expense as reducing the tax base). The fact is that some conditions for recognizing expenses are controversial.
Thus, the Ministry of Finance of Russia, in letter dated August 17, 2006 No. 03-11-02/180, added one more condition necessary for recognizing expenses for the purchase of goods when applying the simplified tax system - the goods must not only be paid to the supplier and sold, but also paid for by the buyer. We note on our own that the last condition does not directly follow from the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The financial department made this conclusion based on an analysis of the provisions of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates the moment of recognition of income.
In "1C: Accounting 8" the user can choose (see Fig. 1): whether to wait for the buyer's payment to be recognized or not. In the latter case, you will have to defend your position in court.

Rice. 1
The main types of expenses and requirements for recognizing these expenses are given in Table 1. The list of requirements for some types of expenses is determined in the form “Accounting policy (tax accounting)” on the simplified tax system tab (see Fig. 1), some of them are mandatory, and some can be adjusted by the user.
Table 1
Type of consumption |
Requirements (expenses are recognized at the latest) |
Third party service reflected |
|
Paid to supplier |
|
Settlements with employees |
Salary accrued |
Wages paid |
|
Calculations for taxes and contributions |
Taxes (contributions) accrued |
Taxes (contributions) are transferred |
|
Materials |
Materials received from supplier |
Materials paid to supplier |
|
Materials transferred to production |
|
The goods arrived from the supplier |
|
Goods paid to supplier |
|
Goods sold to buyer |
|
Goods paid for by the buyer |
|
Additional costs (based on materials) |
Increase the cost of materials and are included in expenses as part of them |
Future expenses |
Deferred expenses reflected |
Paid to supplier |
|
Part of the expenses is written off (only the written-off part can be accepted as expenses) |
|
Intangible assets |
Received NMA |
Paid to supplier |
|
Fixed assets |
Arrival of OS |
OS commissioning |
|
Paid to supplier |
|
Separation of the principal's revenue from income |
When payment is received from the buyer, the payment document is analyzed and if it contains consignment goods, the amount of accepted income is reduced by their sales value. Information about revenue for consignment goods is added to the "Content" field of the KUDiR register entry |
Automatic accounting according to the simplified tax system is provided by several specialized accumulation registers.
Registers are an element of the organization of tax accounting, designed to systematize and accumulate information about the income and expenses of the organization. They record data on the presence and movement of any quantities: material, monetary, etc. The registers used for accounting according to the simplified tax system store information about parties, the state of mutual settlements and balances of unrecognized expenses. Movement through registers is generated automatically when posting documents.
The list of expenses that reduce the tax base for a single tax is determined by Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses are recognized subject to their actual payment. Therefore, control of the status of mutual settlements for tax accounting purposes is carried out in a separate register “Mutual settlements of the simplified tax system”.
To account for expenses subject to tax accounting, the configuration uses the accumulation register "Expenses under the simplified tax system". This register stores information about expenses for which all the conditions necessary for their acceptance for tax accounting have not yet been registered (reflected in the “Income and Expense Accounting Book”). To obtain information about what specific conditions are missing, you can use the "List/Cross-Table" report (menu "Reports" -> "List/Cross-Table"), and in the "Accounting Section" field select the value " Expenses under the simplified tax system."
To move correctly through the registers, you need to pay attention to filling out documents.
The documents may indicate the procedure for reflecting expenses in tax accounting. To do this, use the “Expenses in NU” attribute (see Fig. 2), which can take the following values:
- accepted - expenses comply with the requirements of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- are not accepted - expenses do not meet the requirements of Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- distributed - for organizations transferred to UTII for one or more types of activities. This is how expenses are reflected that comply with the requirements of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and are accepted, but cannot be attributed to a specific type of activity and are subject to distribution.

Rice. 2
If, when an expense is received or written off, the document does not contain the “Expenses in NU” attribute, then the procedure for reflecting expenses in tax accounting is determined by the type of transaction (for example, sale of goods), or the operation is not a tax accounting event (for example, transfer of goods to commission).
Thus, in general, in order to recognize expenses in tax accounting, it is necessary that:
- the expense was not not accepted according to the conditions of receipt;
- the expense was not unacceptable under the write-off conditions;
- all events provided for recognition as expenses by the norms of Chapter 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation were reflected.
Let's consider how, as a result of the implementation of the 1C:Accounting 8 program, the process of recognizing expenses for purchased goods, expenses for services of third-party organizations and for purchased materials in Absolut-XXI LLC was automated.
Example 1. Recognition of expenses on purchased goods
Goods were received from the supplier LLC "1" for a total amount of 10,000 rubles, according to the advance payment listed earlier.
In accounting, this operation is reflected by the following entries:
1) Document “Outgoing payment order” with the “Paid” checkbox:
Debit 60.02 Credit 51 - 10,000 rub. (advance payment transferred);
2) Document "Receipt of goods and services":
Debit 41.01 Credit 60.01 - 10,000 rub. (goods arrived); Debit 60.01 Credit 60.02 - 10,000 rub. (advance credited).
Let's generate a "List/Cross-Table" report for the accounting section "Expenses under the simplified tax system" to obtain a list of unfulfilled conditions for accepting an expense. For this receipt, the line “Not written off” was created in the amount of 10,000 rubles.
Subsequently, half of the received goods were sold to the buyer LLC "2" for the amount of 15,000 rubles. After posting the document “Sales of goods and services”, the following entries were generated in accounting:
Debit 90.02 Credit 41.01 - 5,000 rub. (Cost written off); Debit 62.01 Credit 90.01 - 15,000 rub. (Revenue received)
In the actual sales report, the second line “Not paid by the buyer” is formed in the amount of 15,000 rubles.
Let's reflect the operation of receiving payment from the buyer in the document "Outgoing Payment Order" with the "Paid" checkbox:
Debit 51 Credit 62.01 - 15,000 rub.
In the report there will be a line for the receipt “not written off” in the amount of 5,000. A line is created in the books of income and expenses for the recognition of expenses for the acquisition of goods and materials in the amount of 5,000 rubles.
Example 2. Recognition of expenses for third-party services and purchased materials
The organization LLC "3" carried out work to repair the car in the amount of 2,000 rubles, including the replacement of spare parts in the amount of 1,000 rubles.
These transactions will be reflected in accounting through the documents “Receipt of goods and services” and will generate the following transactions:
Debit 26 Credit 60.01 - 2,000 rubles; Debit 10.05 Credit 60.01 - 1,000 rub.
In the report on the balances of the register “Expenses under the simplified tax system”, one line is formed for the service provided with the mark “Not paid” in the amount of 2,000 rubles. and the second line for the receipt of spare parts with the mark “Not written off, not paid” in the amount of 1,000 rubles. (see Fig. 3).

Indicated in the "Tax and reporting settings" form.
Object of taxation
The object of taxation is indicated in the “Taxation system” section (Fig. 1).
Picture 1.
In accordance with Art. 346.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the following are recognized as objects of taxation when applying the simplified tax system:
- income;
- income reduced by expenses.
The choice of the object of taxation is carried out by the taxpayer himself, unless the taxpayer is a party to a simple partnership agreement or a trust management agreement (clauses 2, 3 of Article 346.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If an existing organization is switching to the simplified tax system and before the transition the organization applied a general tax system (Fig. 2), then in the settings you must check the box “Before the transition to the simplified tax system, the general tax regime was applied” and indicate the date of transition to the simplified tax system (see Fig. 2).
Figure 2. 
Tax rate
The single tax rate paid in connection with the application of the simplified taxation system is indicated in the “STS” section (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. 
The default tax rate offered depends on the object of taxation. It amounts to:
- 6 percent - for the taxable object “Income”;
- 15 percent - for the taxable object “Income minus expenses”.
If, in accordance with the law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, the tax is paid at a lower rate, the “Tax rate” field indicates the rate at which the tax is paid.
The procedure for reflecting advances from the buyer
The accounting policy parameter "Procedure for reflecting advances from the buyer" sets the default rule for accounting for advances received. It is set for the organization as a whole and can take one of the following values (Fig. 4):
- Income of the simplified tax system;
- Income of the principal.
Figure 4. 
The option "Income of the principal" is available if the functionality "Sale of goods or services of principals (principals)" is enabled (Fig. 5).
Figure 5. 
If the procedure for reflecting advances “Income of the simplified tax system” is selected and when reflecting the advance this order is not changed in the document, then in the register “Book of Income and Expenses (Section I)” income will be recorded for the purposes of the simplified tax system (Fig. 6).
Figure 6. 
If the procedure for reflecting advances is “Committent's Income” or when reflecting an advance this order is established in the document, then in the register “Book of Income and Expenses (Section I)” income will not be recorded for the purposes of the simplified tax system (Fig. 7).
Figure 7. 
Procedure for recognizing expenses
For the tax object “Income minus expenses” in the “STS” section, a group of parameters “Procedure for recognizing expenses” is available with a list of events for recognizing expenses (Fig. 8).
Figure 8. 
Each type of expense has its own list of recognition criteria. Events that must occur for the program to take expenses into account when determining the tax base are marked with check boxes. At the same time, for individual events, the checkboxes are checked and there is no option to remove them. This means that for an expense to be recognized, the event must occur.
Material costs
For material expenses, the mandatory conditions for recognition as expenses that reduce income received are the posting of materials (event "Receipt of materials" and payment (event "Payment of materials to supplier").
The list includes one more event “Transfer of materials to production”. It is present because until January 31, 2008 inclusive, a rule was in force that allowed the cost of paid materials to be included in expenses only as they were written off for production.
According to the current version of paragraphs. 1 item 2 art. 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in order to recognize material expenses for the purchase of raw materials and materials, it is enough to take them into account and pay for them. Thus, in order to account for the costs of purchasing materials in accordance with the current legislation, there is no need to check the “Transfer of materials to production” checkbox.
Expenses for purchasing goods
For expenses for the purchase of goods, the mandatory conditions are the posting of goods (the "Receipt of Goods" event), payment for goods (the "Payment of Goods to Supplier" event) and the sale of goods (the "Sale of Goods" event).
The list of conditions for recognizing expenses for the purchase of goods indicates one more event: “Receipt of income (payment from the buyer).” Until 2010, the position of the Russian Ministry of Finance was that in order to recognize expenses for the purchase of goods, only those goods that were paid for by buyers can be considered sold. However, the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation did not agree with this (decision of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated June 29, 2010 No. 808/10), which prompted the Ministry of Finance of Russia (letter dated October 29, 2010 No. 03-11-09/95) to change its position regarding the moment of sale of goods. Thus, starting from 2011, when setting up the procedure for recognizing expenses, the taxpayer may not check the “Receipt of income (payment from the buyer)” checkbox without fear of tax consequences.
Input VAT
For input VAT amounts, the mandatory conditions for recognition as expenses are the presentation of the tax amount by the supplier (the “VAT presented by the supplier” event) and the payment of the tax (the “VAT paid to the supplier” event).
The list of events contains an additional condition: in order to recognize VAT in expenses, “Expenditures on purchased goods (work, services)” to which they relate must be accepted. Due to the ambiguity of the situation, each taxpayer must independently make a decision on this issue and either leave (the default value) or uncheck the “Accepted expenses for goods (work, services)” checkbox.
Additional costs included in the cost
For additional expenses included in the cost price, the mandatory conditions are their acceptance for accounting (the "Receipt of additional expenses" event) and payment (the "Payment to the supplier" event). Another condition - “Write-off of inventories” (which includes additional expenses) is variable. It must be synchronized with a similar condition for recognizing expenses on inventories.
Customs payments
To recognize customs payments as expenses taken into account when determining the tax base, three conditions are provided.
The first two conditions “The import of goods has been processed” and “Customs duties have been paid” are mandatory. For these conditions, the setting cannot be changed.
The third condition “Goods written off” is variable. The program handles this condition as follows. If the “Goods written off” checkbox is not checked, then customs payments are taken into account in full as expenses (entries about expenses that reduce income received are made in the “Income Book of Income and Expenses (Section I)” register when posting the “Customs customs declaration for imports” document. If the “Goods written off” checkbox is checked, then the inclusion of customs duties in expenses by which income of the current period is reduced is carried out by the routine operation of closing the month “Write-off of customs duties for the simplified tax system”. The amount of accepted expenses in this case is determined in proportion to the cost of goods sold, upon import of which customs duties were paid. If the taxpayer wants to avoid possible claims from the tax authorities, then in the settings for the procedure for recognizing expenses, you need to check the “Goods written off” checkbox (default value).
Tax holiday regime
The laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation may establish a tax rate of 0 percent for taxpayers - individual entrepreneurs first registered after January 1, 2015 and carrying out entrepreneurial activities in the production, social and (or) scientific spheres (paragraph 1, paragraph 4, article 346.20 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
These persons have the right to apply a tax rate of 0 percent from the date of their state registration as individual entrepreneurs continuously for two tax periods. Moreover, if the object of taxation is income reduced by the amount of expenses, the minimum tax provided for in paragraph 6 of Art. 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is not paid.
Types of entrepreneurial activity in the production, social and scientific spheres, in respect of which a tax rate of 0 percent is established, are established by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation on the basis of the All-Russian Classifier of Services to the Population and (or) the All-Russian Classifier of Types of Economic Activities.
When using the right to tax holidays, it should be taken into account that at the end of the tax period, the share of income from the sale of goods (work, services) in the implementation of types of entrepreneurial activities for which a tax rate of 0 percent was applied in the total volume of income from the sale of goods (work) , services) must be at least 70 percent.
The laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation may establish additional restrictions on the application of a tax rate of 0 percent, including in the form of:
- restrictions on the average number of employees;
- restrictions on the maximum amount of income from sales received when carrying out a type of business activity in respect of which a tax rate of 0 percent is applied.
In case of violation of the established restrictions on the application of a tax rate of 0 percent, an individual entrepreneur is considered to have lost the right to apply it and is obliged to pay tax at the tax rates established for “ordinary” taxpayers.
If a user - an individual entrepreneur has the right to apply a tax rate of 0 percent and decides to use this right, then in the tax and reporting settings in the "STS" section you need to check the "Tax holidays" checkbox (Fig. 9).
Dear readers! You can get answers to questions about working with 1C software products on our 1C Consultation Line.
We are waiting for your call!
How to create a book of income and expenses in the 1C Accounting 8.3 program?
For organizations operating on a simplified taxation system, the 1C 8.3 Enterprise Accounting 3.0 program implements the ability to automatically fill out the Income and Expense Accounting Book (KUDiR) based on primary documents. In addition to automatic completion, the program also allows you to fill out the report manually.
Setting up KUDiR in 1C
It is important to know that when drawing up the report, data from the accumulation registers “Book of Income and Expenses (Section I, II, III, IV)” is used - for each section separately.
For organizations where the tax base is determined by the formula income minus expenses, we recall that the procedure for recognizing expenses is determined in the Accounting Policy register, on the simplified tax system tab:
Income accounting
Thus, if, for example, we reflect in the program the receipt of funds to the organization’s current account, then the income is automatically reflected in KUDiR.
Example 1:
- 01.2016 - Received 50,000 rubles from the Counterparty to the organization’s account:

- The Book of Accounting for Income and Expenses for 2016 was formed.
To compile a Book of Income and Expenses in the form of a report, you need to go to the menu Reports – Simplified Tax System – Book of Income and Expenses of the Simplified Tax System:

Expense accounting
As for expenses: first of all, you need to remember the procedure for recognizing expenses (setting up accounting policies).
Example 2.
- On January 1, 2016, funds were written off to pay the supplier:

- KUDiR was formed for 2016:

As you can see, column 5 “Expenses taken into account when calculating the tax base” is empty. At the same time, we remember that according to the procedure for recognizing expenses, before an expense in the form of payment to the supplier is recognized, delivery must be made.
- 01.2016 – goods were received on prepayment in the amount of 11,200 rubles:
- KUDiR was formed:

As you can see, the cost of the received goods was included in the KUDiR. Input VAT, in this case, is displayed as a separate line.
Example 3.
What happens if the prepayment is excluded from the previous example?
- 01.2016 – material received from the supplier in the amount of 4,000 rubles. KUDiR was formed for 2016:

- 01.2016 – 3,000 rubles were paid to the supplier for the material received. KUDiR was formed:

In this example, we once again see that an entry in the Income and Expense Book appears only if the sequence of expense recognition is followed.
What to do if the entry does not fall into KUDiR or the book is not filled out?
In addition to the above program algorithm, it should also be noted that the sequence of documents also plays a role. That is, if first of all the delivery was reflected in the system, and then payment was made “retroactively”, then re-posting of delivery documents is required, for example, so that the entry appears in KUDiR (this only applies to non-compliance with the sequence of entering documents into the system, or adjusting the amounts of documents) .
If we talk about fixed assets and intangible assets, then the corresponding records will appear in KUDiR only after the OS is put into operation or intangible assets are accepted for accounting.
As for records that should not appear in the report, there may be various options, for example:
- Also, the sequence of documents was not followed
- documents were used incorrectly to reflect a business transaction (it is implied that the document should not be used for this transaction, or the type of transaction in the document should be different)
- accounting policy is incorrectly configured
Entering entries into KUDiR manually
To make entries in the Book of Income and Expenses manually, we use the document Entries in the Book of Income and Expenses of the simplified tax system (menu Operations - simplified tax system - entries in the book of income and expenses of the simplified tax system).
Example 4.
- On 04.2016, we will manually reflect the receipt of funds to the organization’s cash desk for PKO:

- Let’s form KUDiR and turn our attention to the second quarter:

The entry is reflected in KUDiR.
Based on materials from: programmist1s.ru
All taxpayers using the simplified taxation system (STS) are required to keep a book of income and expenses (KUDiR). If you do not do this, or fill it out incorrectly, you can receive a considerable fine (Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This book is printed and submitted to the tax office upon their request. It must be sewn and numbered.
Before you start creating this income and expense accounting book in 1C 8.3, check the program settings. If you have problems with the formation of KUDiR and some expenses do not fall into the book, carefully double-check the settings. Most of the problems lie here.
Where is the income and expense accounting book 1C 8.3? In the "Main" menu, select the "Settings" section.
You will see a list of configured accounting policies by organization. Open the position you need.
In the accounting policy setup form, at the very bottom, click on the “Set up taxes and reports” hyperlink.

In our example, the “Simplified (income minus expenses)” tax system was selected.

Now you can go to the “STS” section of this setting and configure the procedure for recognizing income. This is where it is indicated which transactions reduce the tax base. If you have a question why an expense does not fall into the book of expenses and income in 1C, first of all look at these settings.
Some items cannot be unchecked as they are required to be filled out. The remaining flags can be set based on the specifics of your organization.

After setting up the accounting policy, let's move on to setting up the printing of the KUDiR itself. To do this, in the “Reports” menu, select the “STS Book of Income and Expenses” section of the “STS” section.
The ledger report form will open in front of you. Click on the "Show Settings" button.

If you need to detail the records of the received report, check the appropriate box. It is better to clarify the remaining settings with your tax office, having learned the requirements for the appearance of KUDiR. These requirements may vary between inspections.

Filling out KUDiR in 1C: Accounting 3.0
In addition to the correct settings, before generating KUDiR, it is necessary to complete all operations for closing the month and check the correctness of the sequence of documents. All expenses are included in this report after they are paid.
The D&R accounting book is generated automatically and quarterly. To do this, you need to click on the “Generate” button in the form where we just made the settings.
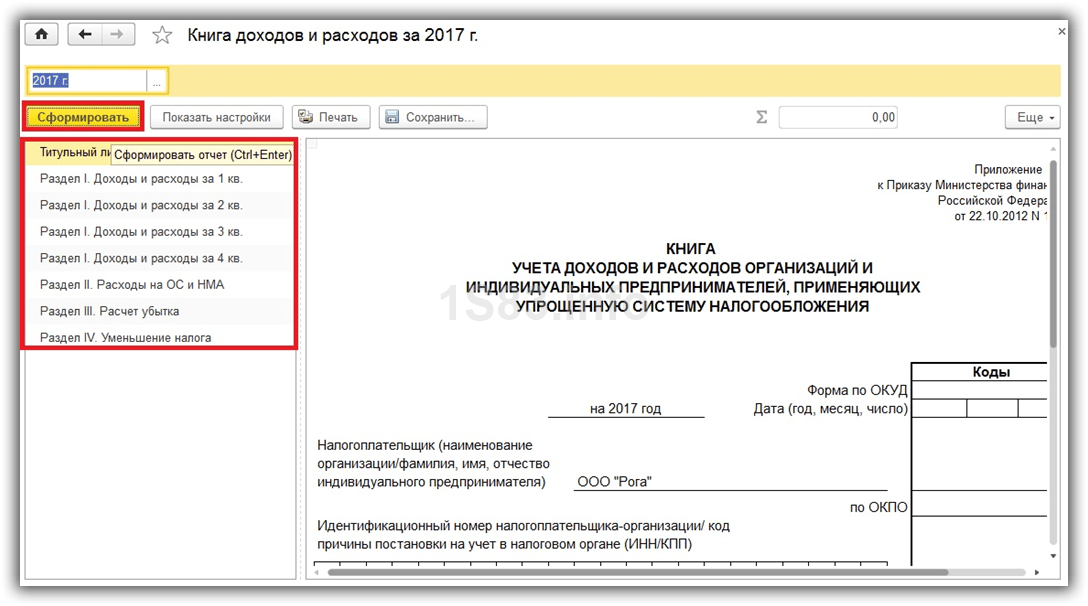
The book of income and expenses contains 4 sections:
- Section I. This section reflects all income and expenses for the reporting period quarterly, taking into account the chronological sequence.
- ChapterII. This section is filled out only if the simplified tax system is “Income minus expenses”. This contains all costs for fixed assets and intangible assets.
- ChapterIII. This contains losses that reduce the tax base.
- ChapterIV. This section displays amounts that reduce tax, for example, insurance premiums for employees, etc.
If you have configured everything correctly, then KUDiR will be formed correctly.
Manual adjustment
If, after all, KUDiR is not filled out exactly as you wanted, its entries can be corrected manually. To do this, in the “Operations” menu, select “STS Income and Expense Book Entries.”

In the list form that opens, create a new document. In the header of the new document, fill in the organization (if there are several of them in the program).

This document has three tabs. The first tab corrects the entries in section I. The second and third tabs are in section II.
If necessary, make the necessary entries in this document. After this, KUDiR will be formed taking into account these data.
Analysis of accounting status
This report can help you visually check whether the book of income and expenses is filled out correctly. To open it, select “Accounting analysis according to the simplified tax system” in the “Reports” menu.

If the program keeps records for several organizations, you need to select in the report header the one for which the report is needed. Also set the period and click on the “Generate” button.

The report is divided into blocks. You can click on each of them and get a breakdown of the amount.
